Introduction:
Alcohol is one of the most commonly consumed substances worldwide, with a significant cultural and social presence. While moderate alcohol consumption may not pose severe health risks for many individuals, excessive or chronic use can lead to various health complications. One such complication is the disulfiram reaction, a potentially serious interaction between alcohol and disulfiram, a medication used in the treatment of alcohol dependence. In this blog, we delve into the dynamics of alcohol consumption, the disulfiram reaction, its effects on the body, associated risks, and strategies for management.
Alcohol Consumption:
Alcohol, chemically known as ethanol, is a central nervous system depressant that affects neurotransmitter activity in the brain. It is commonly found in beverages such as beer, wine, and spirits. When consumed, alcohol can induce feelings of relaxation and euphoria by altering brain chemistry. However, its effects are dose-dependent, and excessive consumption can lead to impairment of motor skills, cognitive function, and judgment. Chronic alcohol abuse can result in addiction, liver disease, cardiovascular problems, and mental health disorders.
Disulfiram and Its Mechanism of Action:
Disulfiram (brand name Antabuse) is a medication used in the treatment of alcohol dependence. It works by inhibiting the enzyme aldehyde dehydrogenase, which is responsible for metabolizing alcohol in the body. As a result, when a person taking disulfiram consumes alcohol, acetaldehyde, a toxic byproduct of alcohol metabolism, accumulates in the body. This buildup of acetaldehyde leads to the disulfiram reaction, which manifests as a range of unpleasant symptoms.
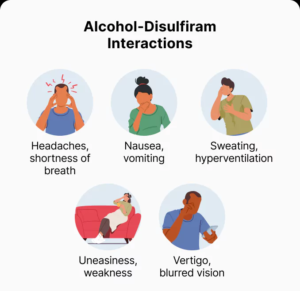
The Disulfiram Reaction:
The disulfiram reaction occurs when alcohol is ingested while disulfiram is present in the body. The reaction typically begins within 10-30 minutes of alcohol consumption and can last for several hours. Symptoms of the disulfiram reaction may include:
1. Facial flushing
2. Headache
3. Nausea and vomiting
4. Sweating
5. Increased heart rate
6. Hypotension (low blood pressure)
7. Respiratory distress
8. Mental confusion
These symptoms can vary in severity depending on the amount of alcohol consumed and individual factors such as age, weight, and overall health. In severe cases, the disulfiram reaction can lead to cardiovascular collapse, respiratory failure, and even death, although such instances are rare.

Risks Associated with the Disulfiram Reaction:
While the disulfiram reaction can serve as a deterrent to alcohol consumption in individuals undergoing treatment for alcohol dependence, it also poses certain risks. One of the primary concerns is the potential for accidental exposure to alcohol-containing products or hidden sources of alcohol. Substances such as cough syrups, mouthwashes, and some food items may contain alcohol and trigger a disulfiram reaction if ingested concurrently with disulfiram.
Another risk factor is non-compliance with treatment regimens. Some individuals may deliberately skip doses of disulfiram or discontinue treatment altogether to avoid experiencing the adverse effects of the disulfiram reaction. Such behavior can undermine the effectiveness of treatment and increase the likelihood of relapse into alcohol abuse.
Management Strategies:
Effective management of the disulfiram reaction involves a combination of patient education, monitoring, and supportive care. Healthcare providers prescribing disulfiram should thoroughly educate patients about the potential consequences of consuming alcohol while taking the medication. Patients should be advised to read product labels carefully and avoid all forms of alcohol-containing substances.
Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential to monitor patient progress and address any concerns or challenges related to disulfiram therapy. During these visits, healthcare providers can assess medication adherence, evaluate treatment efficacy, and provide additional support or resources as needed.
In cases where the disulfiram reaction occurs, symptomatic management may be necessary to alleviate discomfort and ensure patient safety. This may involve administering medications to control symptoms such as nausea, headache, or hypertension. In severe cases, medical intervention may be required to stabilize the patient and manage complications.

The disulfiram reaction is a well-documented phenomenon that highlights the complex interactions between alcohol and medication. While disulfiram can be an effective adjunctive treatment for alcohol dependence, its use requires careful management and monitoring to minimize the risk of adverse reactions. Healthcare providers play a crucial role in educating patients about the potential consequences of alcohol consumption while taking disulfiram and implementing strategies to support treatment adherence and safety. By understanding the dynamics of the disulfiram reaction and implementing appropriate management strategies, healthcare professionals can help individuals with alcohol dependence achieve and maintain sobriety while minimizing the risk of harmful consequences.

Contact Us
Contact Rupantran Neuropsychiatric Center for comprehensive mental health care. Our dedicated team offers personalized treatment plans for various conditions, including depression, anxiety, and addiction. With compassionate support and evidence-based therapies, we prioritize your well-being. Reach out today for expert guidance towards a healthier mind and life.